Introduction to Biology Corner’s Animal Cell Coloring Resource
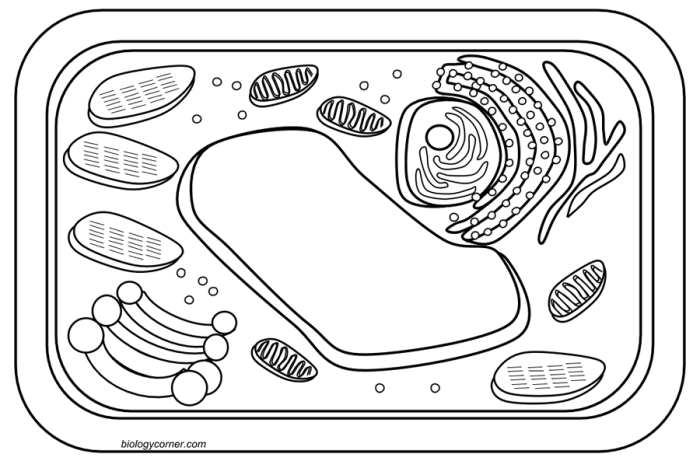
Biology corner.com animal cell coloring – Biology Corner’s animal cell coloring resource offers a dynamic and engaging way for students to learn about the intricate structures and functions of animal cells. Interactive coloring activities go beyond passive learning, transforming the process of understanding complex biological concepts into an active and memorable experience. By actively engaging with the visual representation of the cell, students are more likely to retain information and develop a deeper comprehension of the subject matter.Biology Corner’s approach emphasizes a clear and accurate depiction of the cell’s components.
The coloring activity is designed to be more than just a simple coloring exercise; it’s a guided exploration of the cell’s organelles, highlighting their individual roles and relationships within the larger cellular system. The resource provides detailed labels and descriptions for each organelle, enabling students to connect the visual representation with the corresponding function. This approach fosters a strong understanding of the cell’s overall structure and its dynamic processes.
Target Audience for the Animal Cell Coloring Resource
This educational resource is primarily designed for students in middle school and high school (grades 6-12), aligning with typical biology curricula. The resource can also be effectively utilized in introductory college-level biology courses or as a supplementary learning tool for homeschooling environments. The complexity of the information presented is tailored to be accessible to a wide range of learning styles and abilities within this age group, promoting both visual and kinesthetic learning.
The resource’s clear labeling and straightforward instructions ensure that students with varying levels of prior knowledge can successfully engage with the material. For younger students, the activity can serve as an introduction to basic cell structures, while older students can utilize the resource to reinforce their understanding and delve into more complex details.
Analysis of Animal Cell Components Featured
The Biology Corner animal cell coloring page provides a simplified yet informative representation of a typical animal cell, highlighting key organelles and their relative positions. Analyzing these components allows for a better understanding of the intricate workings of the cell as a whole and the specialized functions of its individual parts. This analysis will detail the organelles depicted, their functions, and a comparison of their roles.
The coloring page likely depicts a selection of the major organelles found within an animal cell. These organelles work together in a coordinated manner to maintain cellular homeostasis and carry out various essential life processes. Understanding their individual functions and how they interact is fundamental to grasping cellular biology.
Organelle Descriptions and Functions
The animal cell, as depicted, likely includes the following organelles: the nucleus, the cytoplasm, the cell membrane, ribosomes, mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum (both rough and smooth), Golgi apparatus, lysosomes, and possibly vacuoles (though these are typically smaller in animal cells than plant cells).
The nucleus houses the cell’s genetic material (DNA), controlling gene expression and regulating cellular activities. The cytoplasm, the gel-like substance filling the cell, provides a medium for cellular processes. The cell membrane, a selectively permeable barrier, regulates the passage of substances into and out of the cell. Ribosomes synthesize proteins, crucial for cellular structure and function.
Mitochondria, often called the “powerhouses” of the cell, generate ATP (adenosine triphosphate), the cell’s primary energy currency. The endoplasmic reticulum (ER), a network of membranes, plays a role in protein and lipid synthesis and transport. Rough ER is studded with ribosomes, while smooth ER lacks them and is involved in lipid metabolism. The Golgi apparatus modifies, sorts, and packages proteins and lipids for secretion or transport within the cell.
Lysosomes contain enzymes that break down waste materials and cellular debris. Vacuoles, if present, function in storage and transport.
Comparison of Organelle Functions
Let’s compare the functions of the nucleus, mitochondria, and ribosomes. The nucleus dictates cellular activities by controlling gene expression, providing the blueprint for protein synthesis. The mitochondria provide the energy (ATP) necessary to carry out these activities. Ribosomes are the protein synthesis machinery, building the proteins encoded by the nuclear DNA using the energy supplied by the mitochondria.
Essentially, the nucleus provides the instructions, the mitochondria the power, and the ribosomes the construction workers.
Summary Table of Animal Cell Organelles
| Organelle Name | Function | Description in Coloring Page |
|---|---|---|
| Nucleus | Contains DNA; controls cell activities | Likely depicted as a large, centrally located, round structure. |
| Mitochondria | Generates ATP (cellular energy) | Probably shown as small, oval or bean-shaped structures scattered throughout the cytoplasm. |
| Ribosomes | Synthesize proteins | May be depicted as small dots, possibly clustered on the rough endoplasmic reticulum or free in the cytoplasm. |
| Cell Membrane | Regulates passage of substances into and out of the cell | Represented as the outer boundary of the cell. |
| Golgi Apparatus | Modifies, sorts, and packages proteins and lipids | Likely shown as a stack of flattened sacs near the nucleus. |
| Endoplasmic Reticulum (Rough & Smooth) | Protein and lipid synthesis and transport | Rough ER may appear as a network of membranes with ribosomes attached; smooth ER might be a less granular network. |
| Lysosomes | Break down waste and cellular debris | May be depicted as small, membrane-bound sacs. |
| Vacuoles (if present) | Storage and transport | If present, shown as small, membrane-bound sacs, likely smaller than those in plant cells. |
Pedagogical Approach and Learning Outcomes
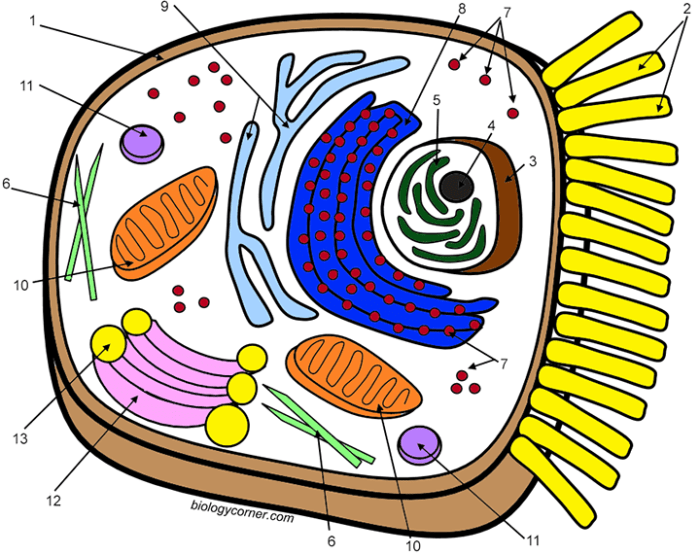
Visual learning aids, particularly coloring pages, offer a unique and effective approach to teaching complex biological concepts. They cater to diverse learning styles, transforming the often-abstract world of cell biology into a tangible and engaging experience for students. The process of coloring actively involves the student, fostering deeper understanding and improved knowledge retention compared to passive learning methods.Coloring an animal cell promotes active learning by requiring students to actively engage with the material.
The act of identifying and coloring each organelle necessitates a thorough understanding of its function and location within the cell. This hands-on approach transforms the learning process from a passive reception of information into an active construction of knowledge. The visual association created through coloring strengthens memory pathways, leading to improved knowledge retention and recall. Studies have shown that incorporating visual aids significantly improves student comprehension and performance in science subjects.
For example, a study published in the Journal of Educational Psychology demonstrated that students who used visual aids in learning biology concepts scored significantly higher on post-tests compared to those who learned through traditional methods.
Effectiveness of Visual Learning Aids in Biology Education
The effectiveness of visual learning aids, such as coloring pages, stems from their ability to bridge the gap between abstract concepts and concrete representations. The process of coloring allows students to visualize the three-dimensional structure of the animal cell and the spatial relationships between its various organelles. This visual representation enhances understanding, making complex information more accessible and memorable.
Furthermore, the act of labeling the organelles reinforces their names and functions, leading to improved recall and comprehension. This multi-sensory approach caters to various learning styles, making it a particularly effective tool for kinesthetic learners who benefit from hands-on activities.
Active Learning and Knowledge Retention through Coloring
The coloring activity facilitates active learning by transforming passive learning into an interactive experience. Instead of simply reading about the components of an animal cell, students actively participate in constructing their understanding through the visual representation. This active engagement promotes deeper processing of information, leading to enhanced comprehension and knowledge retention. The act of coloring itself encourages students to focus their attention on the details of the cell, reinforcing the learning process.
Furthermore, the repetitive nature of the activity, focusing on individual organelles, enhances memorization. This is supported by the concept of spaced repetition, a well-established learning technique where repeated exposure to information at increasing intervals improves long-term retention.
Short Quiz to Assess Student Understanding
The following quiz assesses student understanding of animal cell components, based on the information presented in the coloring page:
- What is the function of the cell membrane?
- Name three organelles found within the cytoplasm.
- What is the role of the nucleus?
- What is the function of the mitochondria?
- What is the difference between the rough endoplasmic reticulum and the smooth endoplasmic reticulum?
Integration of the Resource into Lesson Plans
Teachers can integrate this animal cell coloring page resource into their lesson plans in several ways. It can be used as a pre-activity to introduce the topic of animal cells, engaging students before formal instruction. Alternatively, it can serve as a post-activity to reinforce learning after a lecture or discussion. The coloring page can also be used as a formative assessment tool, allowing teachers to gauge student understanding before moving on to more advanced concepts.
Finally, it can be a valuable homework assignment, encouraging students to review and solidify their understanding of animal cell structures and functions at their own pace. For example, teachers could incorporate the coloring activity into a larger unit on cell biology, using it as a bridge between theoretical concepts and practical application. The quiz could then be used as a formative assessment, providing immediate feedback to students and guiding further instruction.
Comparison with Other Educational Resources
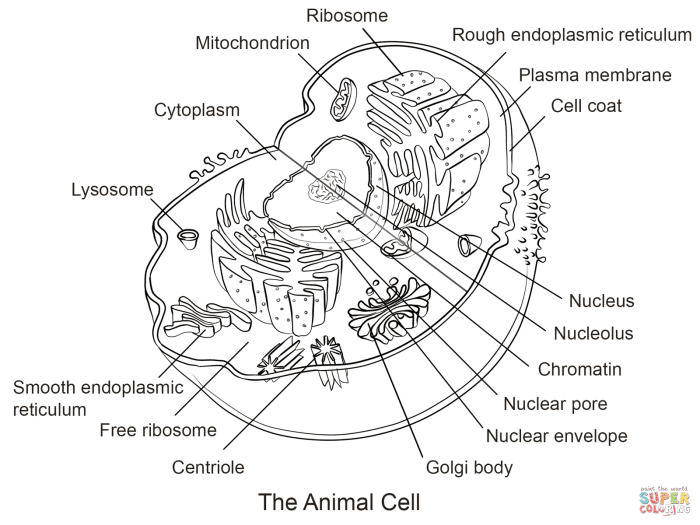
Biology Corner’s animal cell coloring page occupies a specific niche within the broader landscape of online and textbook-based educational resources for learning about animal cell structure. A direct comparison reveals both its strengths and weaknesses when juxtaposed against alternatives. This analysis focuses on key differences in content, presentation, and pedagogical approach.
Several online resources and textbooks offer similar animal cell diagrams and activities. Some provide interactive 3D models, while others use detailed illustrations with extensive labeling. Textbooks often integrate cell structure within broader chapters on cell biology, connecting the concept to related topics like cellular processes and functions. Online resources vary greatly in quality and depth, ranging from simple coloring pages to complex simulations.
Content Comparison
A key differentiator lies in the level of detail provided. Biology Corner’s page presents a simplified representation of an animal cell, focusing on major organelles. In contrast, some resources offer more detailed diagrams, including less prominent structures and even variations in cell types. Certain textbooks might incorporate microscopic images alongside diagrams, providing a more realistic visual representation. Other online resources may offer interactive elements such as quizzes or games to assess understanding.
Presentation Differences
The presentation style significantly impacts the learning experience. Biology Corner’s coloring page employs a straightforward, printable format. This simplicity can be advantageous for younger learners or those who prefer a hands-on approach. However, more advanced resources might utilize interactive features, animations, or 3D models to enhance engagement and comprehension. Textbooks often integrate diagrams within a larger textual context, providing explanations and connections to broader biological concepts.
Some online resources leverage multimedia elements like videos and audio narrations to further improve accessibility and engagement.
Educational Approach Variation
Biology Corner’s approach is primarily visual and hands-on, relying on the act of coloring to reinforce learning. This method is effective for visual learners and can aid memory retention. However, other resources may adopt a more comprehensive approach, integrating various learning modalities. For example, some online resources use interactive simulations that allow students to manipulate virtual cells and observe the effects of different processes.
Textbooks frequently combine visual aids with textual explanations, providing a more holistic learning experience. Some online resources incorporate formative assessment tools, enabling students to immediately check their understanding.
Visual Representation and Design Considerations: Biology Corner.com Animal Cell Coloring
The visual design of Biology Corner’s animal cell coloring page plays a crucial role in its effectiveness as an educational tool. A well-designed coloring page can significantly enhance student understanding and engagement with complex biological concepts. Conversely, a poorly designed page can lead to confusion and hinder learning. The success of the coloring page hinges on its ability to clearly and accurately represent the intricate structures within an animal cell.The current coloring page likely employs a simple color scheme, perhaps using pastel shades to avoid overwhelming the viewer.
The layout likely organizes cell organelles in a manner that mirrors their actual spatial arrangement within a cell, although this might be simplified for clarity. The level of detail might vary, potentially showing only the major organelles or including some minor structures depending on the target age group. The effectiveness of this design in conveying information about animal cell structure depends heavily on the accuracy and clarity of the representation.
A simplified depiction, while easier for younger learners, might omit crucial details, whereas an overly complex illustration could be confusing.
Color Scheme and Layout Effectiveness
The effectiveness of the color scheme and layout in communicating the structure of an animal cell is directly related to the accuracy and clarity of the representation. A visually appealing and well-organized layout can greatly improve comprehension. However, an inaccurate or cluttered layout could hinder learning. For example, if the relative sizes of organelles are not accurately represented, or if organelles are inappropriately positioned, this could lead to misconceptions.
Similarly, a color scheme that is too busy or uses colors that are not easily distinguishable could make it difficult for students to identify different organelles.
Suggestions for Visual Design Improvements
To enhance clarity and engagement, several improvements could be made to the visual design.
- Implement a clearer, more visually distinct color scheme for organelles: Using bright, easily distinguishable colors for each organelle will improve identification and memorization. For example, the nucleus could be a light blue, the mitochondria a vibrant red, and the Golgi apparatus a sunny yellow.
- Incorporate realistic size proportions: The relative sizes of organelles should be accurately depicted, reflecting their actual proportions within the cell, as far as possible within the constraints of the coloring page format.
- Add labels and a key: Including labels for each organelle and a separate key defining each color and its corresponding organelle would enhance understanding, particularly for younger learners.
- Use visual cues to show relationships between organelles: For instance, arrows could be used to indicate the flow of materials between the endoplasmic reticulum and the Golgi apparatus.
- Consider adding a scale bar: This would provide a sense of the actual size of the cell and its components.
Improved Illustration of a Mitochondrion, Biology corner.com animal cell coloring
An improved illustration of a mitochondrion would depict its characteristic oblong or bean-shaped structure. The inner membrane would be shown folded into cristae, represented as a series of inwardly projecting folds, giving the inner membrane a ruffled appearance. The space enclosed by the inner membrane (the mitochondrial matrix) would be clearly differentiated from the intermembrane space between the inner and outer membranes.
The color scheme would utilize a gradient, transitioning from a deep crimson at the center to a lighter, almost orange-red at the periphery, representing the high energy density within this organelle. The cristae could be a slightly darker shade of red to emphasize their three-dimensional nature. This detailed representation would effectively convey the complex internal structure of the mitochondrion and its crucial role in cellular respiration.












